Google rankings are a tricky thing to figure out. Google itself declared it was using over 200 factors to rank pages. While it is still unclear what these factors are exactly, we can come to some conclusions and assumptions backed by data. In the previous article, we focussed on the first 50 Google ranking factors. Now we’re going to move on to the next 50.
PAGE-LEVEL FACTORS
While most of the page-level factors were described in the previous article, there are still some left.
51: HTML ERRORS/W3C VALIDATION
Google says that HTML validation doesn’t matter for rankings much. True; if you have a stable, working site, some errors in code won’t affect rankings at all. However, if your code is sloppy and overall messy, the website won’t work properly and that could harm your ranking.
52: DOMAIN AUTHORITY
A controversial ranking factor. Although conjecture over whether domain authority affects rankings or not still rages on; for years, there’s been no clear evidence from Google one way or another. However, it’s safe to assume that Google wants to give users the best experience possible, therefore leading them to websites that are considered the most relevant and trusted. What does domain authority have to do with that? This metric is based on multiple SEO factors (e.g. lots of qualitative links), all with the goal of identifying trustworthy websites. As a result, higher domain authority generally correlates with having a higher ranking, although this is not a rule.
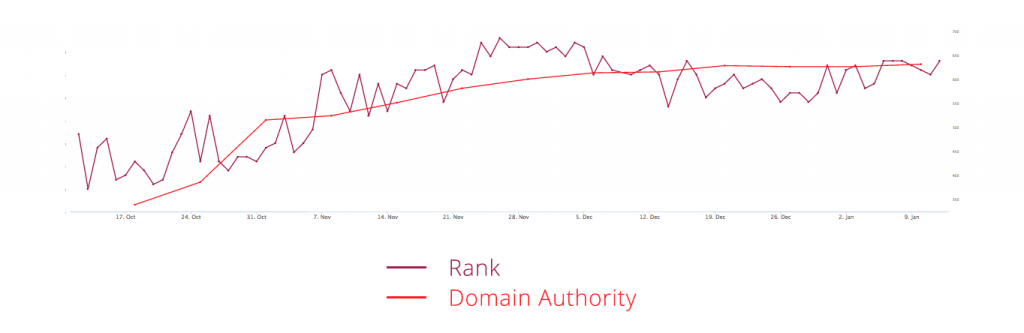
Source: theclickhub.com
53: PARKED DOMAINS
In December 2011, Google released an update that decreased search visibility of parked domains.
54: PAGERANK
Pages with lots of authority tend to outrank pages that don’t have as much link authority. Furthermore, this still matters in 2018.
55: THE NUMBER OF OTHER KEYWORDS PAGES RANK FOR
If a page ranks not only for the main keyword, but also several other ones, this might be considered an internal sign of quality by Google.
56: PAGE AGE
Google prefers fresh, evergreen content in general. In fact, it even allows users to filter results by date. However, if you update some older pages regularly, they might even outperform newer ones.
57: PAGE CATEGORY
It’s crucial for Google to understand the different sections of your site and what they are about. Therefore, a page that’s part of a closely related category might seem more relevant to the search engine than one filed under an unrelated category.
58: PAGE PRIORITY IN SITEMAP
The priority you give to a page via sitemap.xml may influence Google ranking as well.
59: URL LENGTH
This year, Quicksprout researchers calculated the URL length of the top 100 results of 1,000 keywords. According to them, the average length of URLs ranked in the top 10 results is 37 characters. These results clearly show that URLs containing 35–45 characters tend to dominate search results.
60: URL PATH
Those pages that are “closer” to the homepage might get some authority boost over pages buried much deeper in a website’s architecture.
61: KEYWORD IN URL
In 2016, John Mueller called it “a very small ranking factor”. In 2019, you don’t need a keyword in your URL to rank high on Google. However, this doesn’t mean that adding a keyword to your URL won’t affect your ranking at all; it will—it’s just less important compared to other factors.
62: URL STRING
Google reads the categories in the URL string, giving them a thematic signal as to what a certain web page is about.
63: HUMAN EDITORS
This was never confirmed officially. However, Google has filed a patent that allows human editors to influence Search Engine Results Pages (SERPs). Furthermore, this just seems logical as human editors edit content much better than proofreading tools and software, making it easier to read and increasing its quality.
64: WORDPRESS TAGS
Tags on WordPress impacted rankings significantly in the past. Their influence may not be as major today, but specific tags really help to organise and collate your content, making your site much easier for the user to navigate. Tags are like an index for your blog content, and they are not hierarchical in nature. For example, if you run a fashion blog, you may tag specific posts under “1920s silhouettes”, “Karl Lagerfeld”, and “runway models”.

65: REFERENCES AND SOURCES
You should consider citing references and sources in your content. Not only do they tell Google that you put time and effort into your content, they will definitely make your content look more refined and strongly backed by data to users.
66: BULLETS AND NUMBERED LISTS
Google may prefer content with bullets and numbers. Furthermore, using bullets and numbered lists makes it easier for the audience to read or scan through your content, increasing the chances of it getting likes and shares in kind.
67: OUTBOUND LINKS
According to Yoast, outbound links definitely matter for SEO. However, be careful not to add too many when there’s no need to do so. Keep in mind that an excess of outbound links can distract the reader from the main content.
68: USER-FRIENDLY LAYOUT
The Google Quality Guidelines document states that the highest-quality web pages contain content that is immediately visible. This means that if the layout is user-friendly, visitors are much more inclined to navigate your website, make a purchase, and so on. This of course leads to them spending more time on the site, therefore improving your site’s bounce rate and time spent per session—factors Google definitely takes into consideration.
69: USEFUL CONTENT
There’s a possibility that Google can distinguish content quality. If it’s hard for your audience to understand your content, it might not be as useful to them as you think (and therefore isn’t considered as useful by Google). Strive for accuracy, but don’t forget about making your content easy to understand for the target audience.
SITE-LEVEL FACTORS
70: CONTENT THAT OFFERS VALUE AND UNIQUE INSIGHTS
According to Google, sites that contain a limited amount of original content or added value for users could easily be penalised. Therefore, always strive to bring something new or useful to the table.
71: CONTACT US PAGE
We’ve already mentioned the Google Quality Guidelines document before. It also states that Google prefers sites that have an “appropriate amount of contact information”.
72: TERMS OF SERVICE AND PRIVACY PAGES
While these two pages rarely contain very unique information, they still help tell Google that your website is a trustworthy one.
73: TRUST RANK
While some ranking factors become less important over time, TrustRank is still considered valuable by many SEO experts. What is Google TrustRank exactly? It’s a link analysis technique that helps search engines battle web spam. The technique measures “trust signals” that help search engines understand whether or not the content, links, and other ranking signals on a domain are trustworthy.
74: WEBSITE ARCHITECTURE
If your site’s architecture is put together well, it makes it easier for Google to organise your content thematically. Furthermore, it could help Googlebot access all of your site’s pages easily and index all of them. That’s why it’s so important to maximise the site’s architecture for SEO.
75: WEBSITE USABILITY
A site’s usability has everything to do with how much time people spend on it and how often they return to it. Therefore, poor usability can hurt rankings indirectly, leading to a reduction in click rate, page views, and time spent per session on a site.
76: WEBSITE UPDATES
This year, Google denied considering the frequency of updates in their algorithm. However, this could also work as an indirect ranking factor. If you update your content often, people know what to expect from your site and when to come back for more. This could increase the number of site views.
77: WEBSITE UPTIME
No one likes site maintenance periods. They can worsen not only your sales, but your SEO as well. The information about downtime killing SEO has been around for many years, and this most likely won’t change in the near future.
78: WEBSITE REPUTATION AND REVIEWS
This one is simple: your reputation matters both for your sales and SEO. Online reviews are as critical to your local SEO strategy as on-site optimisation and building citations.
79: SITEMAP PRESENCE
A sitemap is what helps search engines (Google included) index your page more thoroughly and easily as well. Therefore, it could directly improve your website’s visibility.
80: SERVER LOCATION
This is important in general as it influences the website’s ranking in different regions. Furthermore, it’s extremely important when it comes to geo-specific searches.
81: SSL CERTIFICATE
SSL certificates are small data files installed on a web server to ensure secure connections from server to browser. They are often used to secure money or data transfers (credit card transactions, logins, etc.). At present, they are a major signal as to the trustworthiness of a domain. Most browsers will warn users about entering sites without an SSL certificate, which can be a huge deterrent. It’s like driving down a road and seeing a “do not proceed” sign, then continuing to do so anyway. Having an SSL cert means the domain prefix HTTPS will feature when users visit your site. Google admits that HTTPS is a ranking factor, but only as a tiebreaker when all the other quality signals between two sites are equal.
82: DUPLICATED META INFORMATION ACROSS THE WEBSITE
When you duplicate meta information across the site, this could affect the page’s visibility in a negative way. Try to avoid it.

83: MOBILE OPTIMISATION
So many people surf the web from their mobile phones these days. Google takes that into consideration when ranking websites. Speed has always been a ranking factor, and if the mobile version of your site is quick to load, it will help the site rank higher on Google. Furthermore, mobile and desktop noticeably differ when it comes to rankings. In today’s current climate, there is simply no reason not to invest time and effort into creating mobile-friendly websites.
84: BREADCRUMB NAVIGATION
Breadcrumb navigation is a user-friendly site architecture that helps both users and search engines understand where they are on a site. Google loves it because it helps them figure out how a website is structured.

Source: cultofweb.com
85: GOOGLE ANALYTICS AND GOOGLE SEARCH CONSOLE
This isn’t confirmed by Google. Still, some believe that if you install these two programs on your website, this can improve the page’s indexing and influence rankings directly.
86: YOUTUBE
It’s no secret that Google owns YouTube. Therefore, it’s safe to assume that YouTube videos get preferential treatment in Search Engine Results Pages (SERPs).
BACKLINK FACTORS
87: LINKING DOMAIN AGE
There’s a possibility that backlinks from aged domains are more powerful than backlinks from new ones. However, factors other than age likely play into this metric. Age often correlates to authority over time, helping a domain build a trustworthy online presence.
88: BACKLINK ANCHOR TEXT
Though it is less important than it used to be years ago, a keyword-rich anchor is still able to affect rankings in a moderate way.
89: THE USE OF ALT TAGS FOR IMAGE LINKS
Search engines aren’t able to read or understand images yet, so it’s the alt tags that provide better image descriptions and context to search engine crawlers. This helps the crawlers index the images more accurately, therefore improving rankings. This also helps new visitors find your website: when they search for a specific keyword in Google image search, Google uses alt tags to render relevant results.
90: THE NUMBER OF LINKING ROOT DOMAINS
This is still one of the most important ranking factors. Keep in mind that earning a couple of links from different websites will affect your ranking more than earning many links from one site, or many links from low-quality sites. Furthermore, links from the websites that have more authority will affect rankings more than the ones coming from less-respected websites.
91: NUMBER OF LINKS FROM SEPARATE CLASS-C IPs
These links can indicate that a wider number of websites are linking to you. This too could improve your rankings.
92: NUMBER OF LINKING PAGES
Even when they come from the same domain, total number of links still has an impact on rankings. This means you can safely add several links from the same domain (website) as long as they are from different individual pages.
93: LINKS FROM .GOV OR .EDU DOMAINS
Some people in the SEO industry doubt that receiving backlinks from such domains really affects rankings. However, top-level domains (TLD) like .gov and .edu still have the trust and domain authority that Google likes. Therefore, receiving links from government or university sites could benefit your rankings.
94: LINKS FROM COMPETITORS
Links coming from other pages ranked on the same SERPs may be considered a valuable ranking factor for a certain keyword.
95: LINKS FROM TRUSTWORTHY WEBSITES
In any industry, there are some sites that are considered the most successful and trustworthy, like Forbes in the business industry. While this might sound controversial, some SEO experts firmly believe that getting linked to from these sites makes Google trust your website more.
96: LINKS FROM UNTRUSTWORTHY WEBSITES
Some websites (also called bad neighbourhoods) have been seriously downgraded by Google over time. There’s a chance that links from these might hurt your site’s rankings.
97: LINKS FROM ADS
Simply buying AdWords won’t help boost your rankings. However, if the AdWords you purchase help you expose content to additional users or influencers, you should consider buying them. While they won’t boost rankings directly, they could indirectly affect other important ranking factors like time spent on your website. Such ads are also a great tool for websites that don’t score well on Google yet, as they ensure a stable number of visitors coming to the website (at quite stable costs as well).
98: AUTHORITY OF LINKING PAGE
This is a sure one. PageRank, or the authority of the referring page, still remains a very important ranking factor. For instance, receiving a backlink from a popular CNN article would be much preferable to that of a fledgling news blog article.
99: AUTHORITY OF LINKING DOMAIN
The authority of the domain you receive links from is also very important. Back to our example above, CNN as an entire website has much more authority than most other small and medium-sized news publications. Therefore, a backlink to your site from this domain will be much more influential.
100: GUEST POSTS
Another controversial factor. Some believe that guest posts aren’t very powerful anymore. Others, however, argue that guest posts can boost SEO if you use them right. Either way, a strong guest post could benefit your site and widen your audience, so it’s worth giving it a shot. These were another 50 Google ranking factors. Curious to learn about the others? Then continue to read our series!


